Oxygen Therapy: What Is It And What Is Its Purpose?

Oxygen therapy is a medically prescribed treatment in which oxygen is administered in high concentrations. In short, its purpose is to treat hypoxia or oxygen deficit in the blood and tissues of the body.
The main indication is the treatment of chronic respiratory failure. However, in recent years, it has been used successfully in the world of aesthetics.
What is oxygen therapy for?
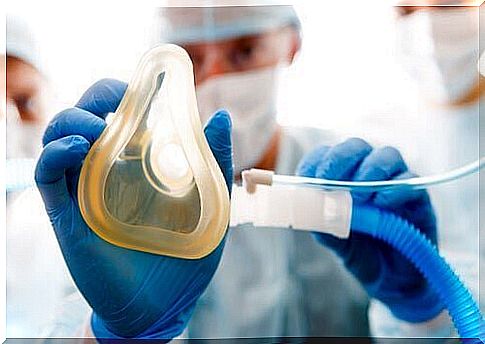
Oxygen therapy especially serves to increase the supply of oxygen to tissues. For this, it makes maximum use of the transport capacity of hemoglobin.
In addition, it reduces some problems and diseases such as chronic bronchitis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is also a good solution for obesity-related hypoventilation and severe asthma.
Oxygen therapy, nowadays, is a good alternative for aesthetic treatments, especially for dry or oily, wrinkled or tired skin. Furthermore, it has been giving good results in the attenuation of dark circles and skin blemishes.
On the other hand, in the world of esthetics, oxygen provides the hydration the skin needs. It also stimulates collagen production and contributes to younger looking skin.
Types
The use of this technique is essential in the treatment of respiratory failure. However, oxygen is administered by prescription. In addition, there are two types of oxygen therapy that are most frequently used:
Normobaric
In normobaric, oxygen is administered at different concentrations. Typically, it is applied in a concentration between 21 to 100%. Furthermore, one of the most common options for its application are nasal cannulas or masks.
hyperbaric
In this type, oxygen is always administered at 100% concentration. In hyperbaric patients, the patient is inside the chamber. Thus, a helmet or a mask is used for its application.
The purpose of this therapy is to increase the supply of oxygen to the tissues via hemoglobin. When the amount of oxygen entering the body is high, it causes pressure in the alveoli that causes the hemoglobin to saturate.
In this way, alveolar oxygen pressure is increased and respiratory and cardiac work are reduced. With this, it is possible to maintain the oxygen pressure constantly.
What complications can oxygen therapy bring?
As with any treatment, there can be complications. In oxygen therapy, complications arise from an inadequate concentration of oxygen. Although they can also arise due to an excess of treatment time.
Among the symptoms that may appear are, for example:
- Tracheitis and bronchitis.
- Deterioration of mucociliary movement.
- Acute lung injury.
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
Furthermore, as a consequence of breathing the dry and cold mixture of gases, dryness and ulceration of the mucous membranes may appear. There may also be deterioration of mucociliary transport, retention of secretions and an increase in their density.
What are the administration routes for oxygen therapy?

When patients are breathing spontaneously, therapy can be delivered through nasal cannulas and masks. Among the masks are included the following:
- Venturi mask. It delivers an exact concentration of oxygen to the patient. During administration, the patient cannot eat or speak. In addition, you may experience the sensation of heat and may experience slight skin irritation.
- Simple breathing mask. It is a soft plastic device that covers the boas and the nose. It has side holes that allow the exhaust of exhaled air. It must fit well to the nose to prevent leakage; Fits snugly on head with elastic strap.
Another route of administration is the low-flow system. This system is suitable for people who have to undergo minimal contact with oxygen.
The high-flow system and the hyperbaric chamber can also be used. However, in patients who lack spontaneous breathing, it is applied by means of a mechanical respirator.